What is GERS?
Global Entity Reference System
The Global Entity Reference System (GERS) is a universal framework for structuring and matching map data across systems. GERS, coupled with Overture datasets, is a potential standard for identifying and referencing the physical and conceptual entities we've defined in our world. It's also a mechanism that can simplify the integration and exchange of data layers.
GERS provides stable identifiers called GERS IDs for real-world geospatial entities across data releases and maintains consistency when entities appear in multiple source datasets.
GERS is a system
The "S" in GERS stands for a system, with the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Overture reference map | consists of the canonical datasets Overture releases each month |
| Global registry of GERS IDs | catalogs all GERS IDs ever published |
| Data changelog | describes changes to entities across releases |
| Bridge files | connects the GERS IDs in a release to the IDs from the underlying source data |
How does GERS work?
-
Overture assigns a unique ID to discrete entities. These could be buildings, road segments, places, or addresses. These IDs are intended to be stable across Overture releases.
-
Overture maintains open-source matching and conflation libraries to ensure that the ID remains stable across releases.
-
Each Overture release is the latest reference map for these IDs.
-
The reference map is global and open.
Using GERS
We envision the Overture ecosystem using GERS in the following ways:
Matching and associating data
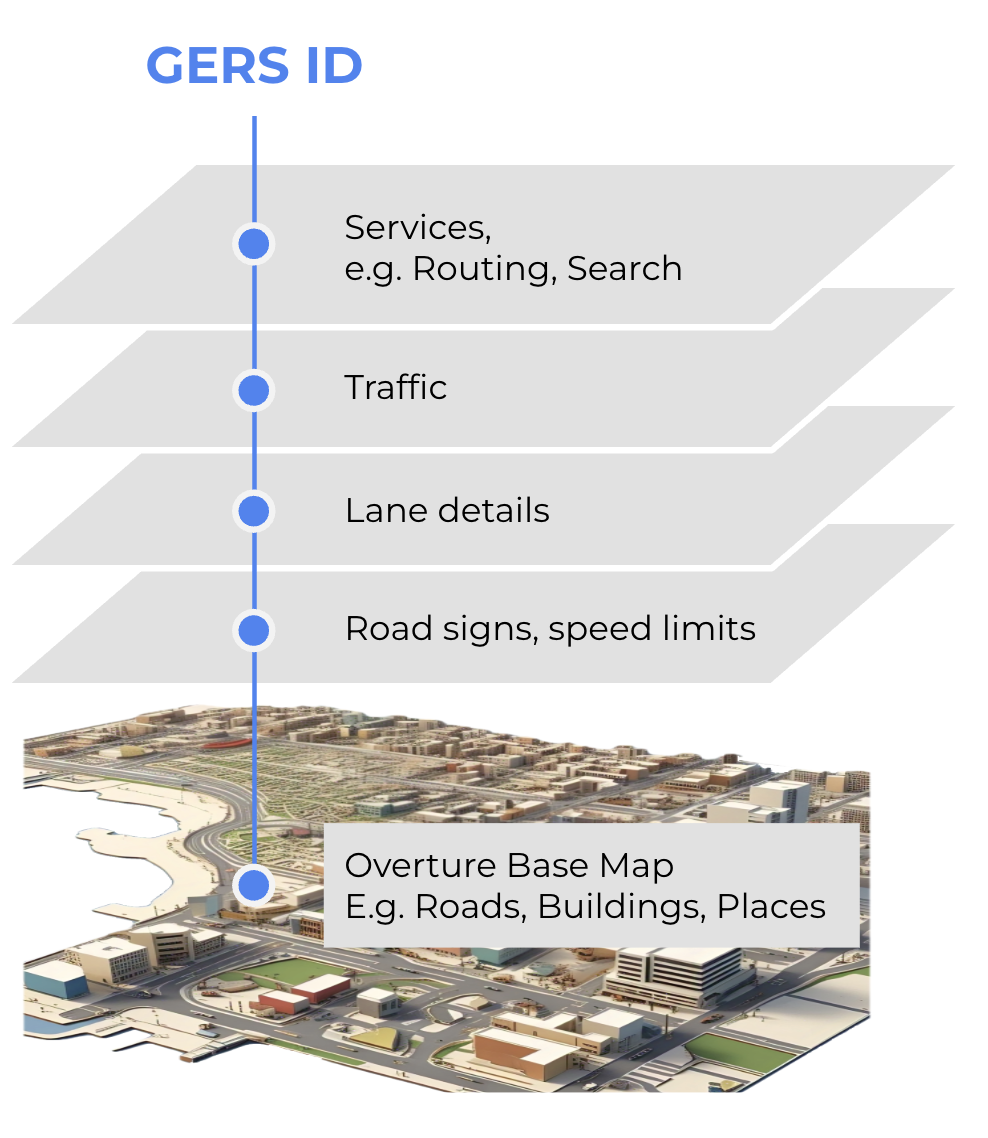
You can independently associate your own data (or a third-party dataset) with Overture data. For example, you might want to link real-time traffic data to Overture road segments, insurance data to Overture buildings, restaurant reviews to features in Overture's places dataset, and socioeconomic data features in Overture's divisions dataset. When third-party data is matched to an Overture feature it picks up that feature's GERS ID and becomes "GERS-enabled" data, ready to be associated via ID to any other GERS-enabled dataset in the Overture ecosystem.
Contributing data
You can contribute data to the Overture Maps Foundation, and we will use Overture's matching algorithms to match the features in your dataset to features in Overture. Matched features may be assigned an existing GERS ID, and we may generate new GERS IDs for new features.